It begins from the female reproductive organs that occur due to uncontrolled outgrowth and spread of abnormal cells.
Types:
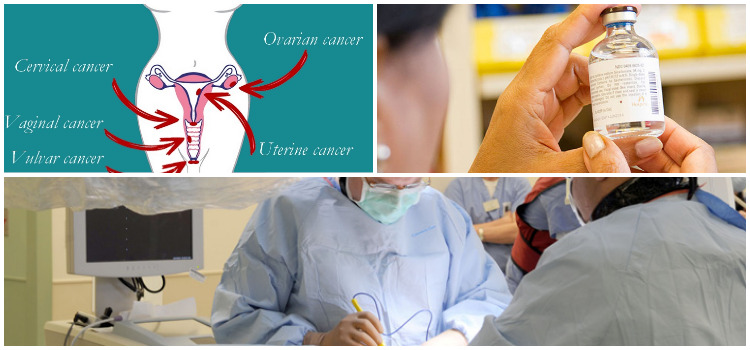
Various types of gynecologic cancers are named as per the affected organ or part of the body where they first originated including cervical, ovarian, uterine/endometrial, vaginal and vulvar cancers.
Cervical Cancer- It begins in the cervix, a lower cylindrical shaped portion of the uterus, its lower region is connected to the vagina.
Ovarian Cancer– It affects the ovaries, a pair of solid oval-shaped organs that produce hormones and eggs (ova).
Uterine Cancer- It originates in the main body of the uterus, a hollow organ where a baby grows during pregnancy.
Endometrial Cancer- It begins in the uterus lining also known as the endometrium and the most common type of uterus cancer.
Vaginal cancer- It starts in the vagina, a tube-like, muscular passage that extends from the external part of the female sex organs (vulva) to the cervix.
Vulval Cancer- It begins in the vulva, the external part of the female reproductive system. The vulva includes the inner and outer lips known as labia minora and labia majora, as well as the opening of the vagina, the clitoris and the mons-pubis- a fatty and soft mound of tissue above the labia.
Other Gynaecological Cancer- It include fallopian tube cancer and gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD), also known as pregnancy-related cancer.
Causes and Risk factors
A reason for various gynaecological cancers is not completely known, but there are some factors associated with the risk of many types of gynaecological cancers. Out of them, a few types can be modified and some other cannot.
Some of these risk factors include:
- Age
- Family history of gynaecological cancer
- Gene mutations
- History of reproductive problem
- Hormonal exposure– As medication or produced by the body
- Diethylstilbestrol (DES) exposure in the uterus
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Infection
- Lifestyle- smoking and excessive body weight
Symptoms
It depends on where the tumor is located, tumour size, and intensity of tumour growth, which includes:
- Abnormal or persistent vaginal bleeding especially after menopause or sexual intercourse
- Unusual vaginal discharge
- Abdominal pain or discomfort
- Abdominal swelling
- Change in bowel or bladder habits
- Pain during sexual intercourse
- Burning, itching, or soreness
- Wart, sores or lumps growth
Diagnosis
A number of tests can be performed to confirm gynaecological cancer, including:
- Physical and pelvic examination
- Pap smear
- Various Blood tests, including- CA125 test
- Imaging tests including, Ultrasound, CT scan, MRI or PET scans
- Biopsy- A tissue sample is taken for cancer examination under a microscope.
Treatment
Gynaecological cancer is usually managed and treated by a multidisciplinary team of doctors, oncologists, and other health professionals.
- Treatment depends on the severity of symptoms, stage, and type of the disease as well as the general health of the patient.
- Treatment involves the diagnosis of its stage (how far cancer may have spread), surgical removal of as much of a tumour as possible, and Radiotherapy, Chemotherapy and Hormonal therapies.
- Some women may be offered to participate in a clinical research trial to find various new ways to diagnose and treat many types of cancer.
Once diagnosed with cancer, it is quite common that you might feel scared, overwhelmed, anxious or upset. So, it is essentially important for you to get support from your friends, and family and other professional societies and organizations who can help you cope with Cancer.
Find a specialist team of doctor, oncologists or a hospital having the expertise to diagnose and treat the specific cancer disease using to advanced technology. You can get a second or third opinion before beginning treatment.
For more information regarding various gynaecological cancers, visit us at Chandigarh Cancer and Diagnostic Center (CCDC) for an expert consultation.
